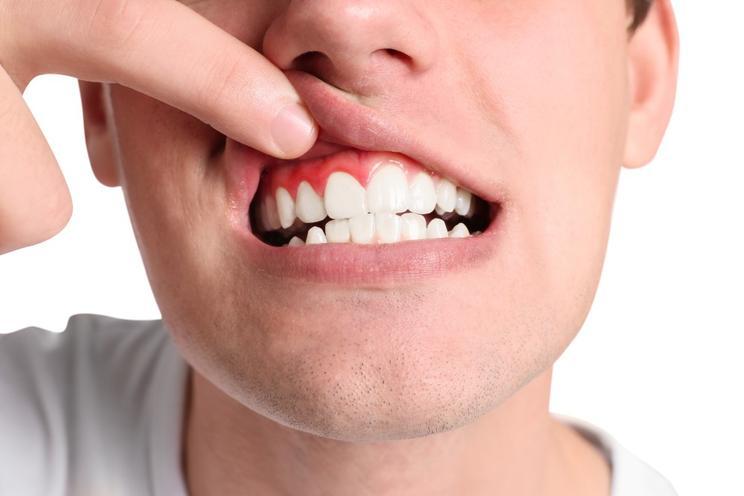
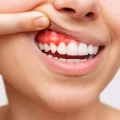
Do you know that? You look in the mirror and think, “My teeth are getting longer.” You calm yourself down by saying, “Oh, I’m just imagining that.” But the impression of receding gums keeps coming back as the months go by, and if you look at older photos of yourself, it will be confirmed. However, this is an optical illusion, because it’s not your teeth that are getting longer – it’s your gums that are becoming “shorter”. More precisely: it retreats. As the gums recede, more of the tooth crowns become visible and the teeth appear longer.
Why do gums recede?
There are basically two main causes of gum recession. The central question is: Is there inflammation or not? If inflammation is not responsible for gum recession, it is a recession (gum recession or gingival recession). This recession can be due to incorrect tooth brushing technique with toothbrushes that are too hard; this is referred to as brushing trauma.
People with very thin gums are also often affected by non-inflammatory gum recession because the fine tissue is not as resilient as thick, strong gums. And the normal aging process also very often results in gum recession. Recession can also have anatomical causes: If the lip frenulum is too tight or the cheek frenulum is attached too tightly to the gums, the pull of the frenum on the gums can be so strong that it gradually retreats. The problem can be easily solved by surgically cutting or moving the ligament. In addition, accidental injuries to the gums or orthodontic treatments can also lead to recession.
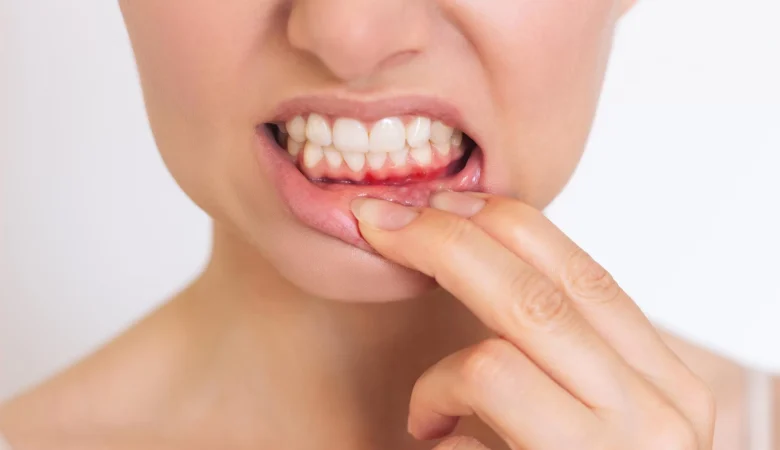
If the cause is inflammation, the diagnosis is usually gingivitis or periodontitis (colloquially known as periodontitis). Gingivitis is an inflammation of the gums. If it progresses and becomes chronic, it is referred to as periodontitis. It’s not just the gums that are affected, but the entire periodontium.
Can gums grow back on their own?
Many affected people ask us whether the gums will recover on their own with good care. You are used to strong self-healing powers in your own body – even larger wounds heal on their own. But unfortunately we have to say: In the case of receding gums, this doesn’t work. The body cannot regenerate the lost gum tissue on its own. Regeneration is only possible if the gums have only been slightly damaged, i.e. not yet completely lost. To do this, the cause of the gum damage must be identified as early as possible in order to be able to take effective measures and give tips on how to properly deal with the gums.
Can receding gums be prevented?
To a certain extent, you can effectively prevent early gum recession. Rule #1 for healthy gums: Carry out your oral hygiene correctly and thoroughly, but at the same time gently. In this way, you avoid brushing trauma that damages the gums and stop the bacteria that can lead to periodontitis. The most important components of oral hygiene are daily cleaning of teeth and interdental spaces at home. Additional professional teeth cleaning in the dental practice is essential, ideally by a qualified dental hygienist. And you should definitely adhere to the recommended check-up dates. More about caring for your gums.